

FSC Forest Management Certification
Through conformance with the robust social, economic and environmental standards within the FSC Principles and Criteria, FSC-certified forest management enhances the well-being of local people, economic viability of the certificate holder, and environmental appropriateness of forest management.
FSC Forest Management (FM) certification is designed to provide a credible guarantee that all Forest Management Units (FMUs) included in the scope of the certificate comply with the requirements of the Forest Stewardship Standard specified on the certificate.
In Malaysia, forests are assessed against the National Forest Stewardship Standard (NFSS) of Malaysia in order to become an FSC FM certificate holder.
The NFSS of Malaysia applies to all types of forest (including forest plantations) operations seeking FSC certification within Malaysia (Peninsular Malaysia, Sabah, and Sarawak), covering all scales and intensities of forest management operations at the Management Unit level. It includes timber and non-timber forest products (NTFPs) such as:
- Fruits (edible or non-edible);
- Sap or gland secretion: gum, resin, latex;
- Medicinal herbs: leaves, rods, barks, roots, mushrooms;
- Stem plants: rattan, bamboo, sap wood, heart wood.

More about FSC FM Certification, including solutions for small-scale/family/community forests (e.g. Group & SLIMF Certification, Continuous Improvement Procedure) and Controlled Materials in the link below.
FSC Ecosystem Services Procedure
Ecosystem services are the benefits that people obtain from nature. Forests provide us with a wide range of benefits, from clean water to productive soil and carbon sequestration. In FSC certified forests, valuable ecosystem services are protected. In 2018, FSC introduced a procedure to demonstrate and make known the positive impact of responsible forest management on ecosystem services. The procedure sets out the requirements for FSC-certified forest managers to credibly demonstrate the impact of their activities on the maintenance, conservation, restoration, or enhancement of ecosystem services.
The FSC-PRO-30-006 Ecosystem Services Procedure builds on FSC forest management certification by allowing forest managers or owners to make specific, credible claims on how their management activities are contributing to maintaining and/or enhancing various ecosystem services in their forests. Impacts can be verified through the following measures:
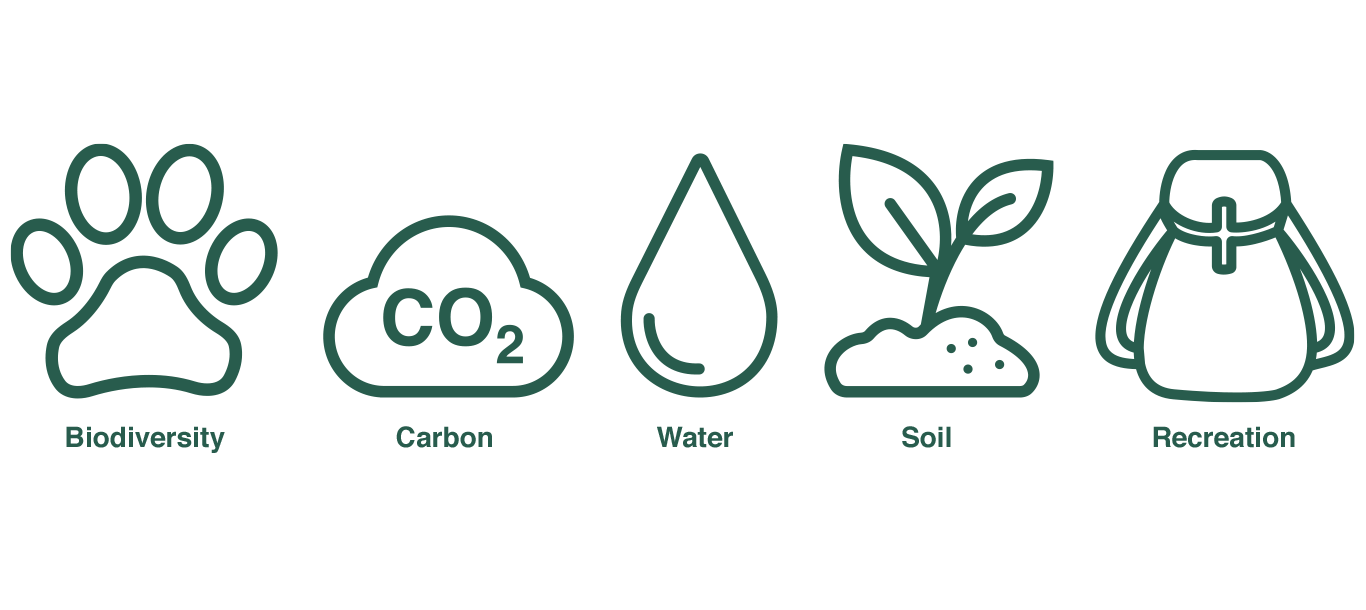
These verified positive impacts aim to facilitate payments for ecosystem services and provide access to other benefits. Hence, adding business value for those who responsibly manage forests and those who take action to preserve forest ecosystem services.
Work in progress: The FSC-PRO-30-006 Ecosystem Services Procedure: Impact Demonstration and Market Tools is currently undergoing a revision, the details of which can be found here.
FSC recently entered into a collaboration with:
1) Verra - to develop tools and processes enabling forest managers and communities to concurrently certify their projects in FSC’s forest management standards and Verra’s Verified Carbon Standard (VCS) Program
2) South Pole - to support and develop nature based solutions projects within forest management-certified areas in Africa and Latin America
Steps towards FSC certification
Overview of the Main Audit / Evaluation Process
- Certification Bodies (CB) are required to conduct all Forest Management evaluations in accordance with FSC-STD-20-007 (v3-0) (Forest Management Evaluations Standard). Evaluation is based on the CB's observations of the means of verification for each Indicator of the applicable Forest Stewardship Standard (for forest management units (FMUs)). In Malaysia, it is the NFSS of Malaysia. The means of verification include study of documentation and records, field observations, and interviews with managers, employees, contractors and other stakeholders. Observations may be collected over a wide area including many different sites and many different means of verification.
- Pre-evaluation: A pre-evaluation is mandatory (before the main evaluation) for the following:
- Plantation larger than 10,000 hectares;
- All non-plantation forest types larger than 50,000 hectares, unless the whole area meets the requirements for classification as a "low intensity managed forest"; or
- FMUs containing high conservation value attributes unless the whole area meets the requirements for classification as a "small forest".
- Preparation: You need to have a management plan, prepare documents and records, set up a management system and document it, assign roles and responsibilities, and ensure the relevant staff receives appropriate training, to conform with the applicable Forest Stewardship Standard.
- Stakeholder consultation: The CB must inform stakeholders (identified according to FSC-STD-20-006 (v3-0) (Stakeholder Consultation for Forest Evaluations Standard) at least six weeks before the start of the main evaluation site visit, details of the evaluation.
- On-site audit/evaluation: Activities include opening and closing meetings with the FMU team, documents and records review, field visits and interviews with stakeholders.
- Audit/evaluation results: The CB prepares a report. Non-conformities (major and minor) are detailed in the report. Any major non-conformity must be addressed and closed before a certificate can be issued. The report undergoes an independent peer review.
If the certification decision is positive, the FMU will receive an FSC certificate code (XXX-FM-000000) and unique FSC trademark licence code (FSC-C000000), which will be published on FSC Public Search Database.
